Without proper understanding you might wonder are 3D printing and injection molding the same? But they are not. While they are both used for producing plastic parts they are done in completely different ways. The aim of this post is to explain how they are different and answer questions like, “Is 3D printing quality equal to injection molding?”, or “Which is cheaper injection molding or 3D printing?” or even, “Is 3D printing more accurate than injection molding?”. Perhaps it’s that you need a better understanding of both 3D printing and injection molding in order to choose which is best for you and your product and, going forward, use this information and knowledge to help reach a decision as to which you should choose. That’s what we will be learning in the following article. What they are, how they can help us, but most importantly, weighing up their pros and cons to determine which is best for you when it comes to injection molding vs 3D printing.
Let’s start with a brief explanation of what they are, and what they can do.
What Is Injection Molding
Injection molding, or plastic injection molding involves a process of making use of molds – often either steel or aluminium. This mold is carved out into the shape of whatever product you ultimately want to design and then it is injected with molten plastic. Once the molten plastic has cooled the mold is then opened and the process is completed. For more information on injection molding, check out our blog page on custom injection molding right here.
What Is 3D Printing
3D printing on the other hand uses what’s known as an additive process. This means that the object is created layer by layer, stacked on top of each other. Because of this process, unlike injection molding there is no mold unit that is required, since nothing needs to be injected into it. The 3D printer simply needs a CAD file (computer aided design) which the machine then loads and starts the building process.
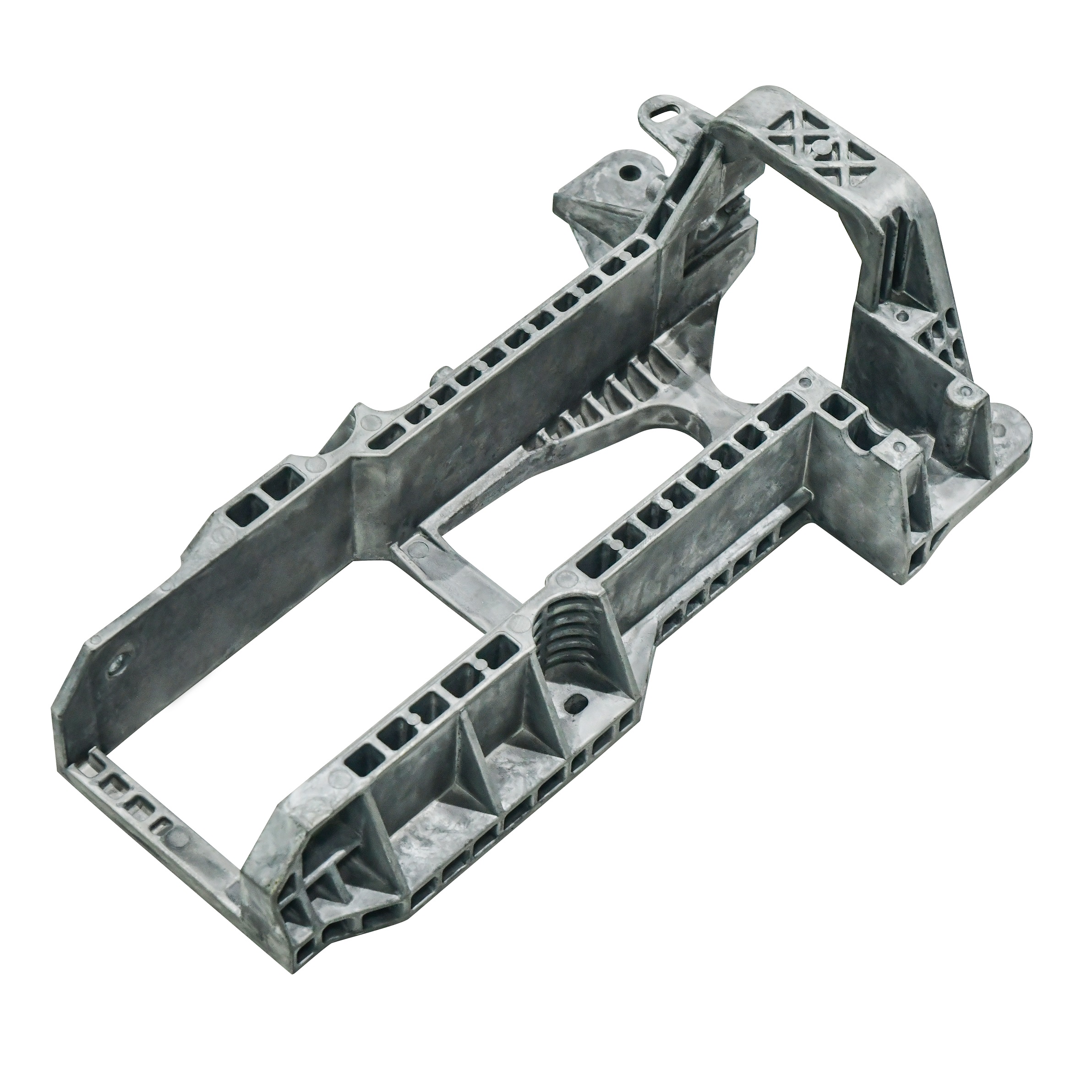
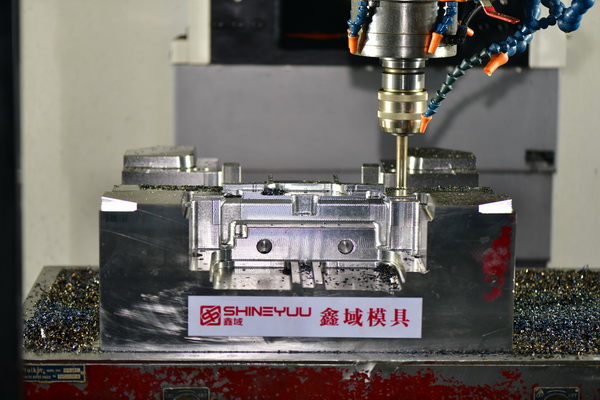
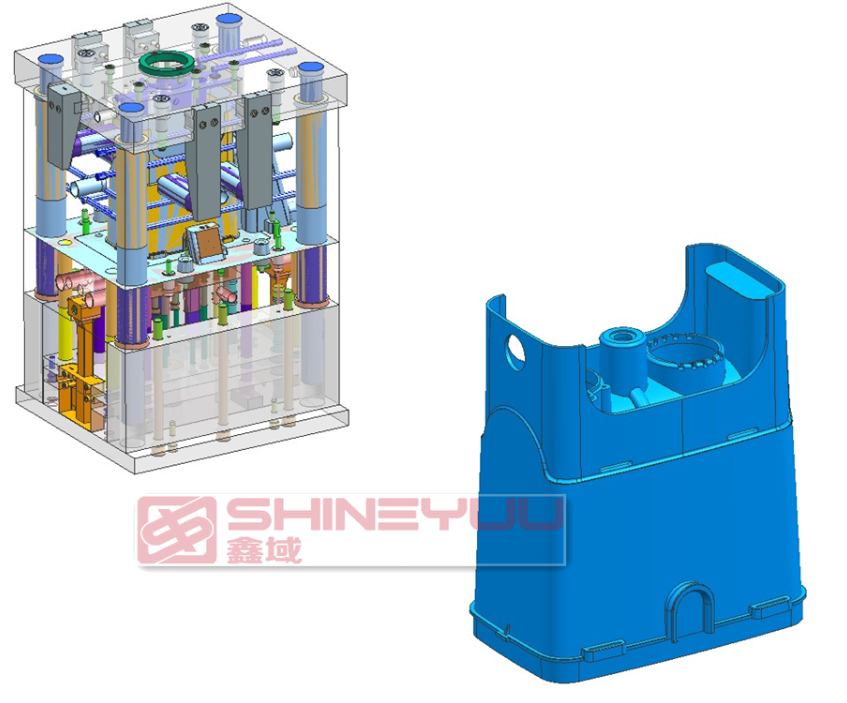
Below you can see both a product and mold that was developed right here at Shineyuu.
3D Printing Vs Injection Molding Price
One of the most important aspects when comparing the two are 3D printing vs injection molding cost. But first, it’s important to understand where those costs come into play. For example, what kind of business or supply are you looking to manufacture for? How many of the products do you expect to produce? One, hundreds, thousands, tens of thousands or even millions? This is a critical question to ask when considering an injection molding 3D printing cost comparison.
So what’s cheaper injection molding vs 3D printing? 3D printing has an extremely low cost to entry. A desktop computer and the supply of materials needed to print are vastly cheaper than the equipment needed for injection molding. The machines of an injection mold can cover tens to even hundreds of thousands. Not to mention the price of the mold itself. The distinct difference however is that 3D printing can be designed for a hobby, whereas injection molding is designed for an industry. Not to mention that the costs of an injection molding machine are offset by manufacturing companies which build the product that you are looking to create, like us here at Shineyuu.
Depending on the number of the same product being built, 3D printing, while also more preferable in smaller numbers becomes increasingly more expensive in larger volumes. This makes 3D printing ideal for something like low-cost prototyping, but inefficient for mass production. This is where injection molding shines in prices, as the same mold can be used even up to millions of times over, and the product still retains its uniform design.
So in summary, 3D printing cost vs injection molding price which is better? Generally 3D printing is a solid go-to for prototyping low volume of parts, whereas injection molding is better for mass production.
3D Printing Vs Injection Molding Strength
Let’s look at 3D printing vs injection molding strength. What is best to choose when it you have to consider the strength of an item, 3D printing or injection molding? When to comes to a completed products’ strength the hands down winner for a physical product is that of injection molding. The reason for this is because objects made through injection molding consist of a single poured layer, which adds overall strength to the shape since there are no fissures or points of weakness. This is contested when it comes to 3D printing however, since it is built layer upon layer, leaving possible room for errors, unless the 3D printing is modified or diluted. So when asking mechanical strength of 3D printing vs injection molding, there is one significant choice.
3D Printing Vs Injection Molding Speed
We must also examine speed of 3D printing vs injection molding. When it comes to injection molds, depending on the plastics used, these molded products can set within a matter of seconds. As well as this, most plastic injection molds can hold multiple pieces, which also multiplies the speed of production time. When you combine this with the fact that injection molding is automated in nature, manufacturers like us can create hundreds of thousands of pieces a day and have products shipped and ready in no time. 3D printing builds layer by layer, and is most effective when orders amount to numbers in their hundreds or less.
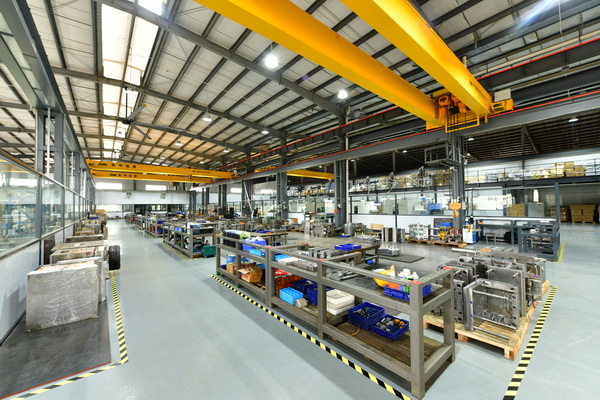
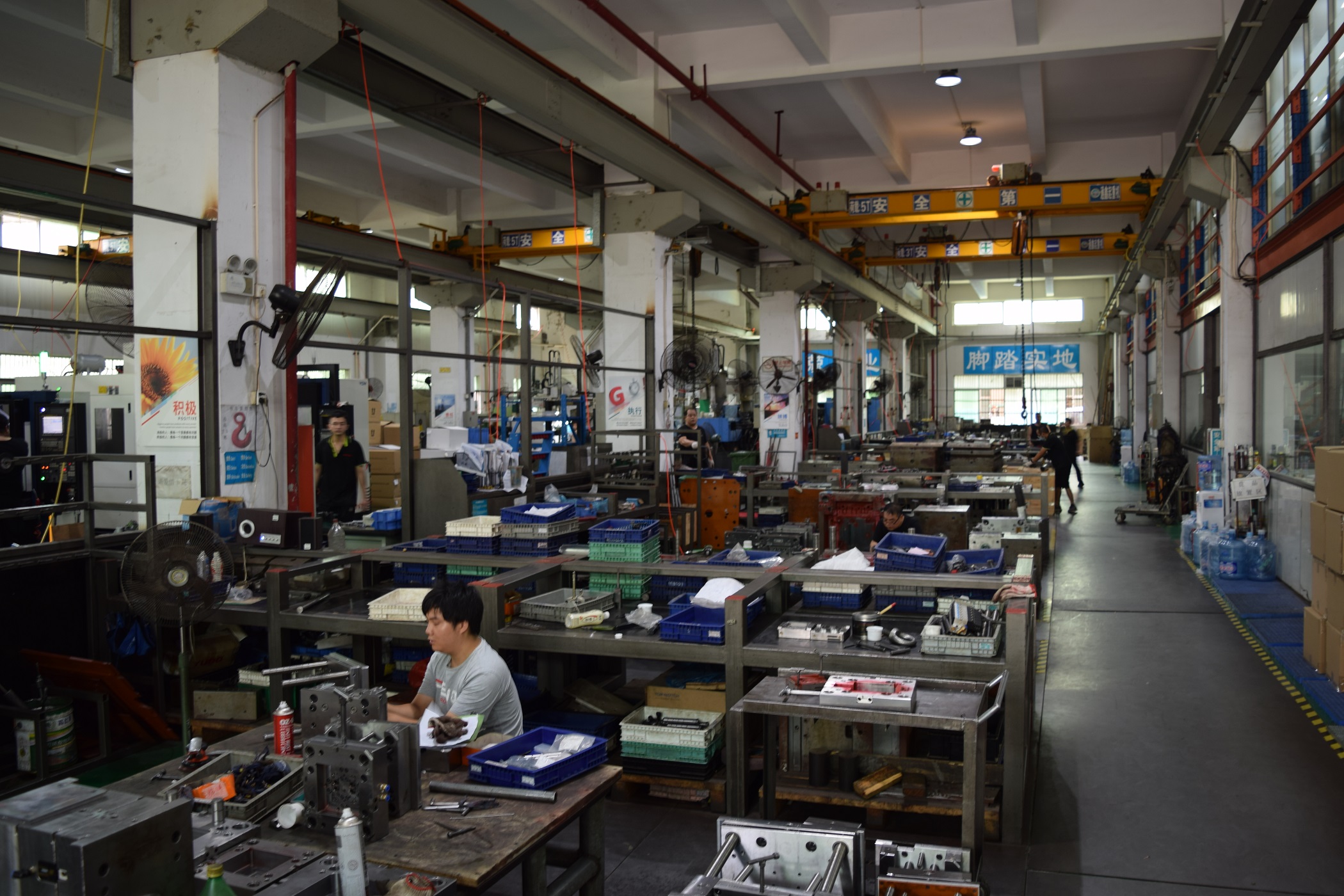
Here is an image of our rapid tooling and injection molding factory:

3D Printing Vs Injection Molding Quality
When looking at 3D printing vs injection molding another important aspect is its quality. Injection molding allows intricate designs to be brought to life with extreme precision, since every millimetre of a mold is filled. This prevents things like segmentation or air bubbles and other critical design flaws, since injection molding is completed with seems or assembly required. So the surface on the product, otherwise known as finishing surface, remains smooth. This when compared to 3D printing is one of the most significant differences between the two, as 3D printing is at an extreme disadvantage. The quality of a 3D printed product can often be unattractive in appearance. 3D printing can leave visible ridges from its layers and other structural faults during its manufacturing, which wouldn’t be found with plastic injection molding. When looking at 3D printing injection molding complex parts, both are capable of doing a good job, however for 3D printing those ridges may remain.
Advantages of 3D Printing
Let’s look at why 3D printing is superior to injection molding, by going through some of its key advantages.
Flexibility: 3D printing is excellent for making iteration upon iteration. When you compare this with injection molding, making dramatic changes can be quite costly since it would involve creating an entirely new mold to start the process all over again. This is not the case with 3D printing. You can pause a construction even mid process in order to make design changes, you do not need to start the production run from the beginning all over again.
Low Cost: A 3D printer and the materials needed to produce a product is vastly cheaper than an injection molding machine and the mold required to build the product. This fact makes 3D printing something anyone can get into from hobbyists to small businesses looking to experiment. Is injection molding cheaper than 3D printing? Yes, but only at larger volumes.
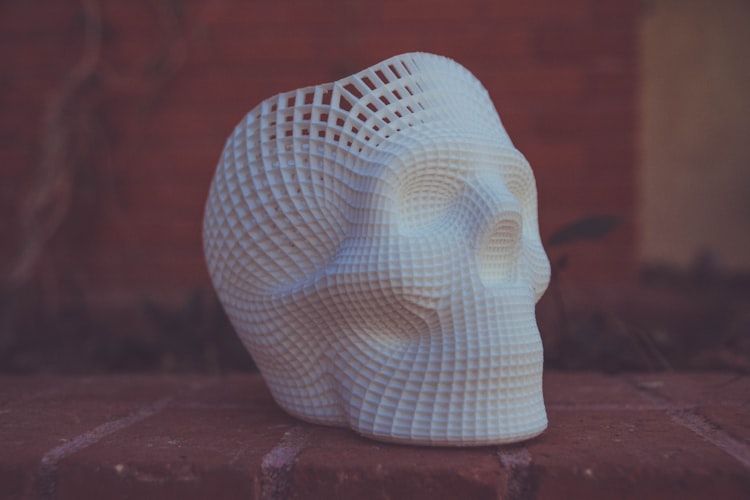
This cool skull was made via 3D printing:
Advantages of Injection Molding
We’ve looked at some of the advantages of 3D printing, now let’s take a look at some of the benefits of injection molding:
Product quality: We’ve already discussed the advantages of injection molding when comparing the two, but it seems on speed, strength and overall quality injection molding cannot be beaten. When people wonder will 3D printing replace injection molding, maybe one day in the far-flung future, but for now these reasons are why injection molding remains the manufacturing industries standard.
Low Unit Costs: Once an injection mold is made, the process of reproducing a prototype is fairly simple. The same part can be reproced hundreds of thousands to even millions of times and the parts will retain the same kinds of uniformity throughout. This method is also far more cost-effective in higher production sizes, as they see lower per-unit expenses.
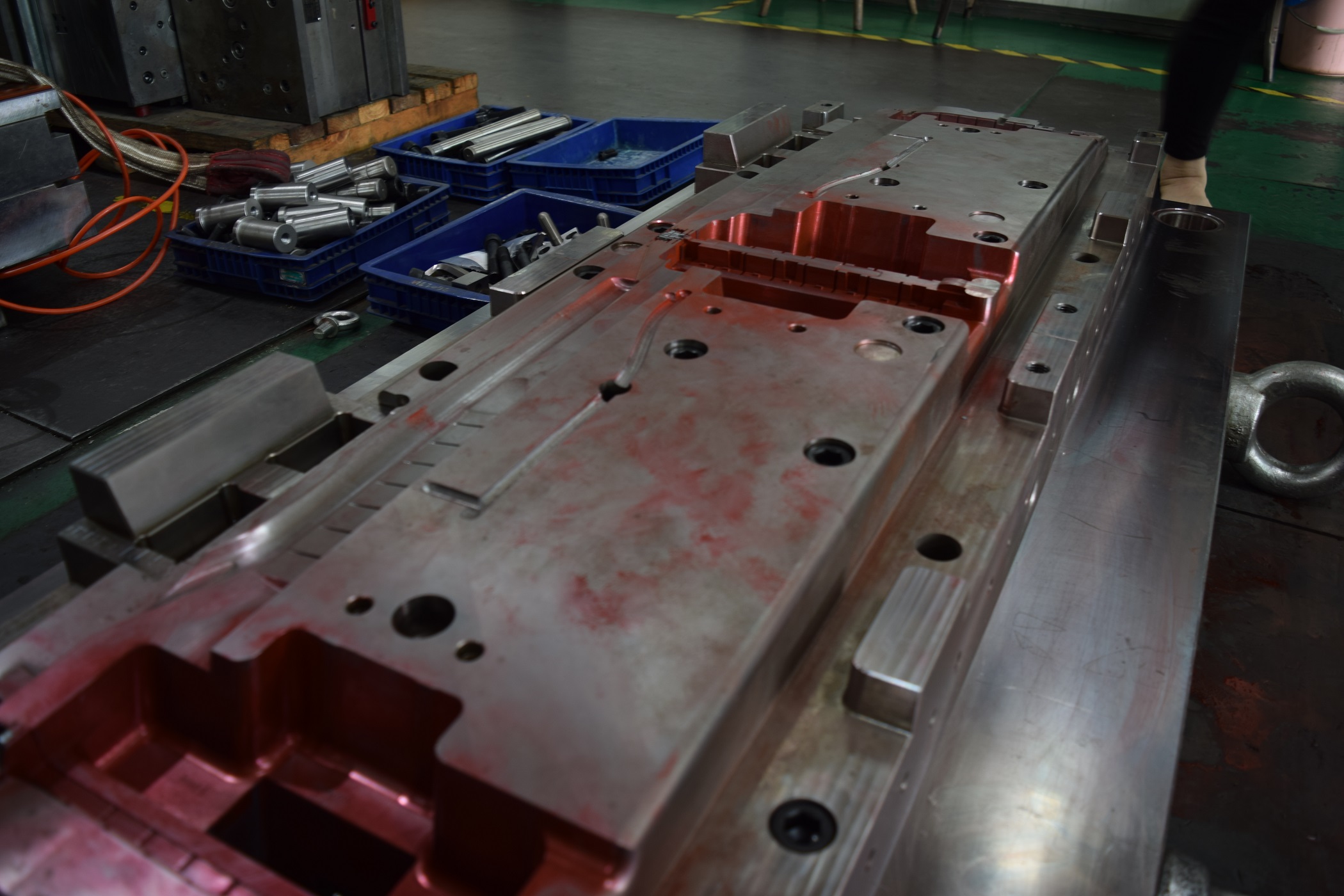
Here is a large mold built right here at Shineyuu, ready for producing parts:

Disadvantages of Both
So we looked at the strength of 3D printing vs injection molding, but what about their weaknesses? Completely opposite to their advantages, let’s take a brief look at their disadvantages.
Injection molding can be seen as inflexible, considering how timely and expensive it is to recreate a mold and also needing to restart a product’s design and scratch when changes need to be made. It’s also more expensive when comparing the two.
3D printing products are not as impressive on a quality level when compared to that of injection molding, and when it comes to pricing for larger volume parts, such as in the thousands ranging to millions it is also considered more expensive. Is industrial 3D printing faster than injection molding? No. Will 3D printing replace injection molding? Maybe one day, but for now it is still preferable to create parts in lower numbers.
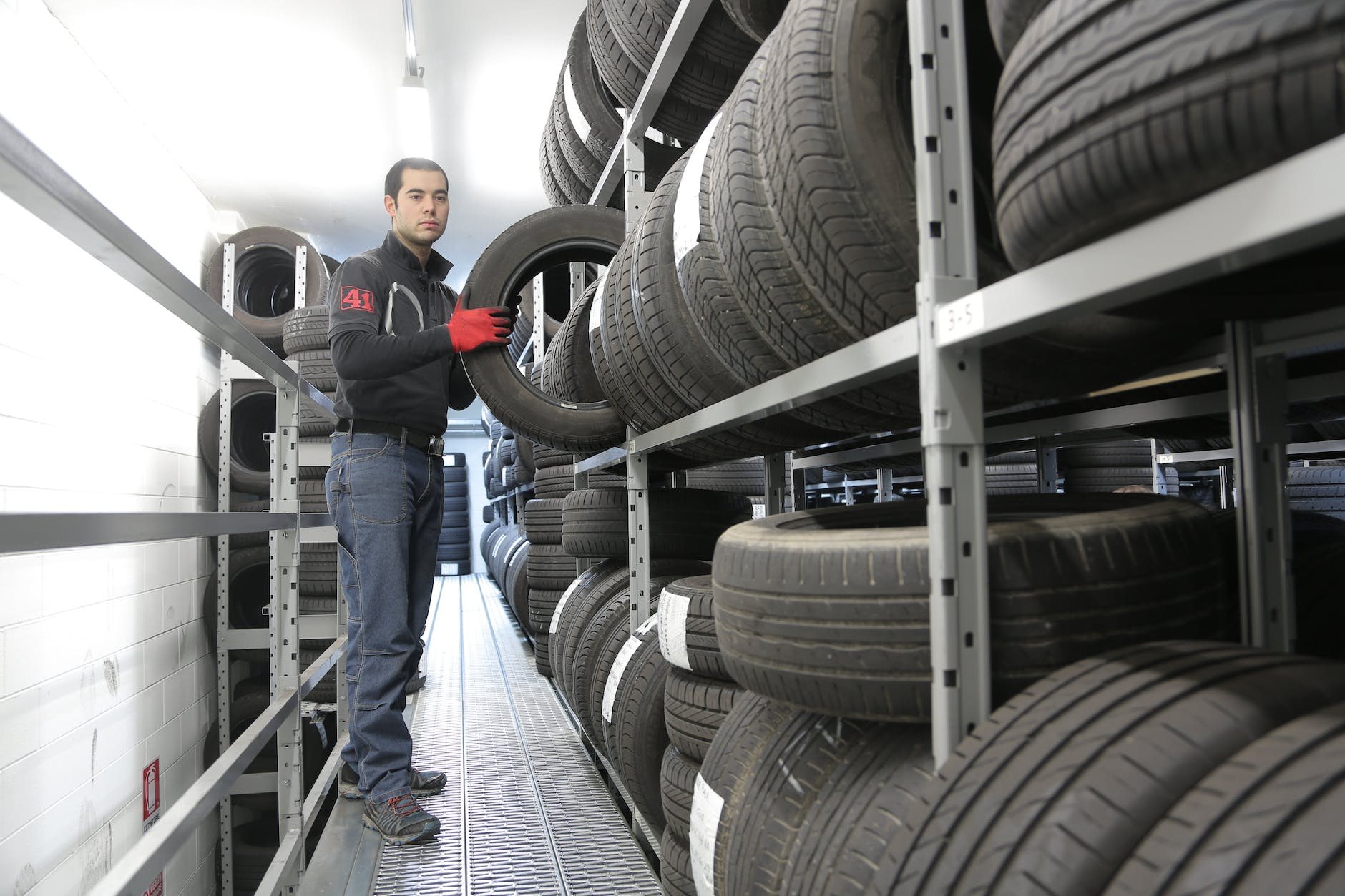
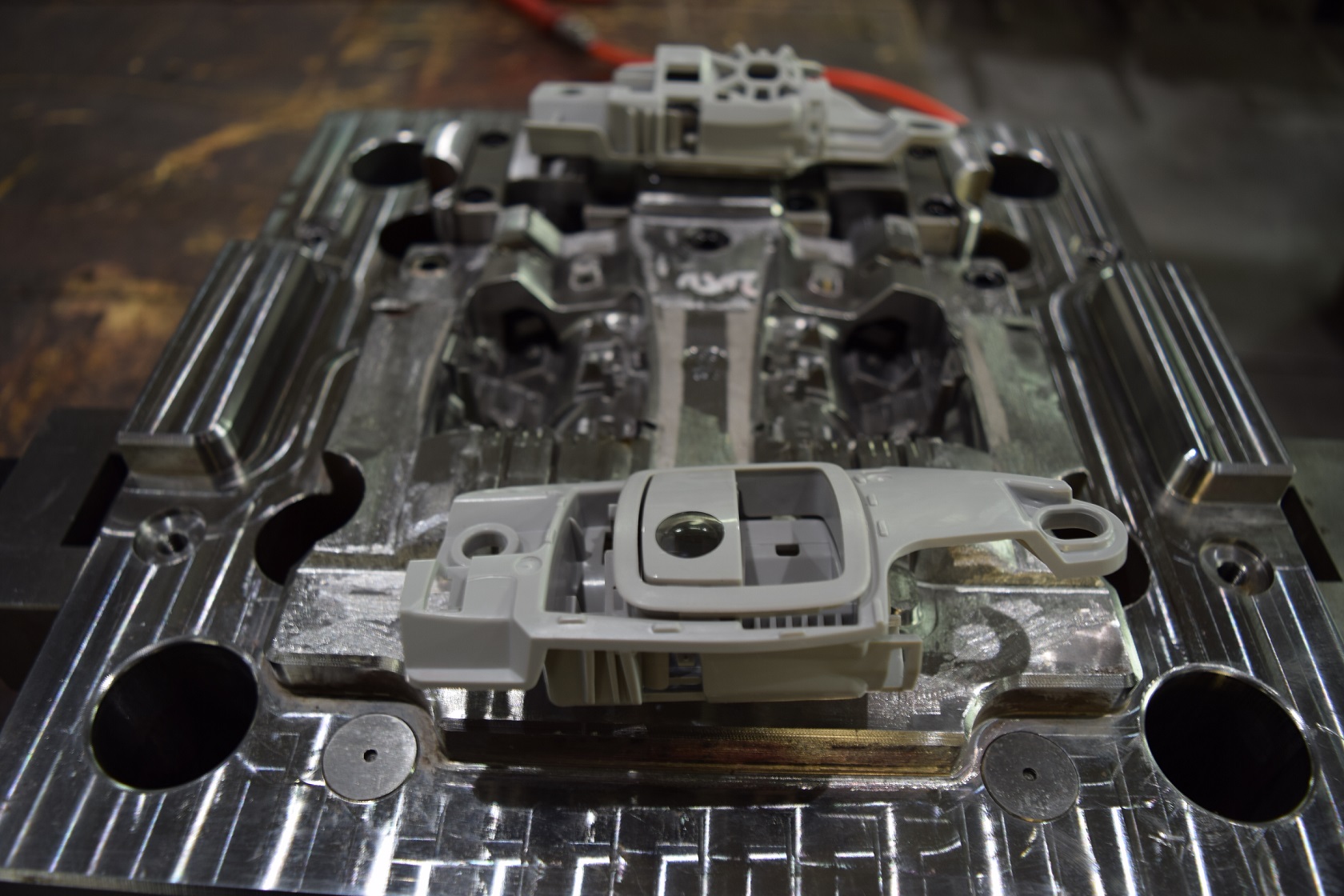
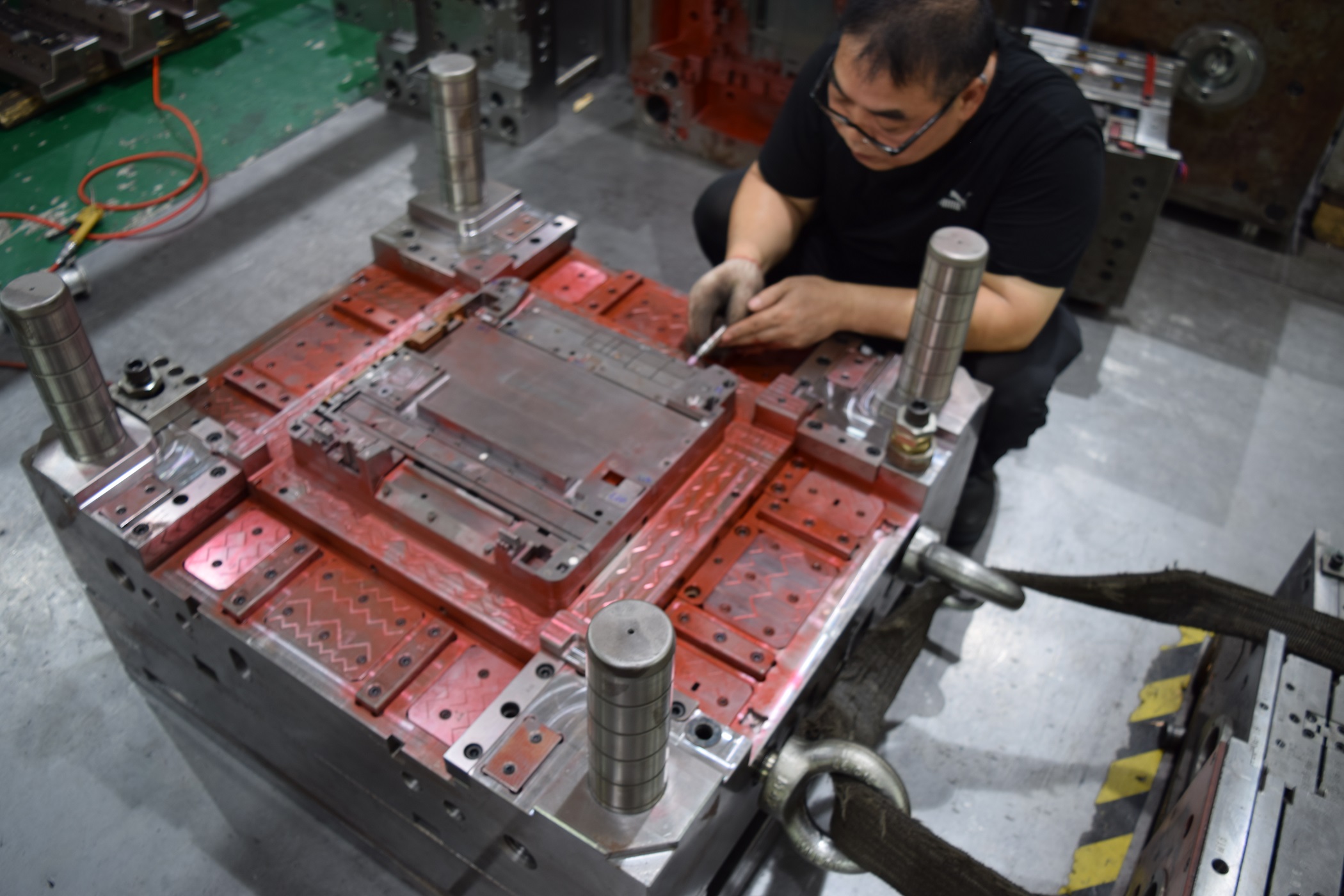
Here an employee at Shineyuu fits and checks an injection mold:

When To Use 3D Printing & Injection Molding
So here is a brief summary of the things we have learned and covered in this article about 3D printing injection molding.
When it comes to 3D printing materials vs injection molding strength, we had found that since injection molding is made in one continuous piece there are no fissures or points of weakness, making injection molding the stronger choice. As we looked at 3D printing vs injection molding quality we uncovered the fact that injection molding gives a clean, polished and smooth surface finish whereas 3D printing has visible ridges an may contain structural faults. If wondering is 3D printing faster than injection molding, we looked at the fact that injection molding is built for automation at its core, and that a single mold can create multiple pieces at the same time which can significantly speed up production.
However, when looking at injection molding vs 3D printing cost at lower volume parts, such as for prototype building, we found that the price difference between a piece in 3D printing and injection molding leans in favour of 3D printing. This is because the price of the materials and machine cost less than that of an injection molding machine and mold. So when is 3D printing more expensive than injection molding? At higher volumes, since injection molding is made for mass production. This means at higher numbers injection molding is the way to go, from thousands of product parts and upwards.
Some have suggested that they can also be used together, so exactly how 3D printing and injection-molding can work in tandem? One key possibility is 3D printed molds for injection molding. If the part has high temperature resistance, 3D printing can actually be a viable source of 3D printed molds for injection molding or can even be used as an injection molding prototype with 3D printing. One can also consider a 3D printing injection molding tool, and since traditional molding tools are often made with aluminium or steel this may be a cheaper pricing point and injection molding 3D printing may become more commonplace in the future.
Conclusion
I hope you’ve found this article to be useful, and that you have learned the difference between injection molding and 3D printing, along with their unique advantages and flaws with injection molding vs 3D printing. The comparison for 3D printing vs injection molding is one that may become ever similar in the future, but for now they have their own key advantages and best times for use. And any question like when to switch from 3D printing to injection molding, should become clear when you look at the volumes needed from a humble hobby to a full-scale production. There are still some other key factors we should look towards in the future, such as environmental issues like carbon emissions 3D printing vs injection molding, but they are for another time.